
BUS FPX 4014 Assessment 5 Inventory and Ordering Decisions
Student Name
Capella University
BUS-FPX4014 Operations Management for Competitive Advantage
Prof. Name
Date
Question #1
Calculate and provide the numeric monthly aggregate production rate rounded to a whole number. The level production rate is the total units per period. The formula for the Aggregate Production Rate (APR) is:
APR=M(D1+D2+D3+D4+D5+D6−SI+EI)
Given:
- Six-Month Demand (= 1,535)
- Period 1 (= 240)
- Period 2 (= 225)
- Period 3 (= 265)
- Period 4 (= 270)
- Period 5 (= 260)
- Period 6 (= 275)
Net Requirement (= 1,535 + 50 – 150 = 1,435)
Monthly APR =(240+225+265+270+260+275−150+50)6=239=6(240+225+265+270+260+
275−150+50)=239 (rounded).
Question #2
What is the equation for the number of workers needed to meet the aggregate production rate?
168=48 units per month per worker. 4831=1.6 units a day per worker.3148=1.6 units a day per worker. 23131=7.45 units a day.31231=7.45 units a day. 7.451.6=4.66 daily workers.1.67.45=4.66 daily workers. 4.66×31=145 workers needed to produce 231 units in one month.4.66×31=145
workers needed to produce 231 units in one month.
Question #3
Provide the algebraic equation for the economic order quantity rounded to the closest whole number.
EOQ=(2×OC×UHCAQ) ���=(2×10×54002)=54,000EOQ=(2×10×25400)=54,000 54,000=23254,000=232
Question #4
Provide the algebraic equation for the reorder point.
RP=DQ×LT ��=22×5RP=22×5 ��=110RP=110
Question #5
Describe the below forecasting methods and the math associated with each method, along with the pros and cons of using it.
Naïve
- Estimating technique used as a comparison without adjusting.
- Pro: Easy, quick, benchmarking.
- Con: Accuracy, cannot forecast turning points.
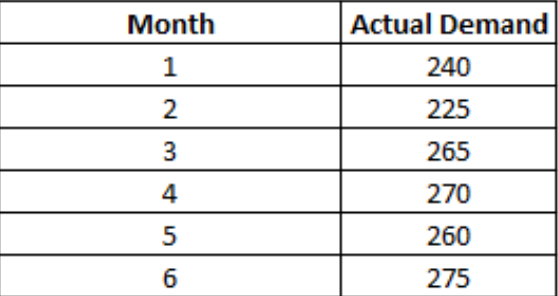
Simple Mean
- An average of all available data.
- Pro: Easy to calculate, easy to use for patterns.
- Con: No actual value, as only averages provided.
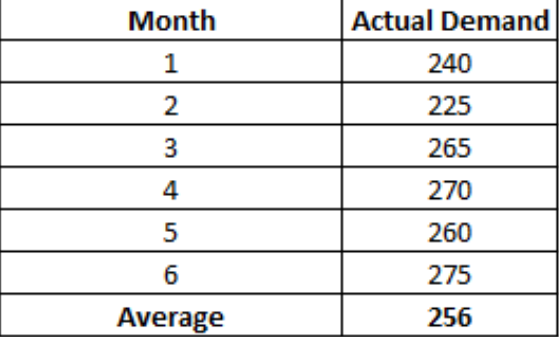
Simple Moving Average
- Takes recent actual values and then averages them.
- Pro: Easy to calculate and understand.
- Con: All values are calculated equally.
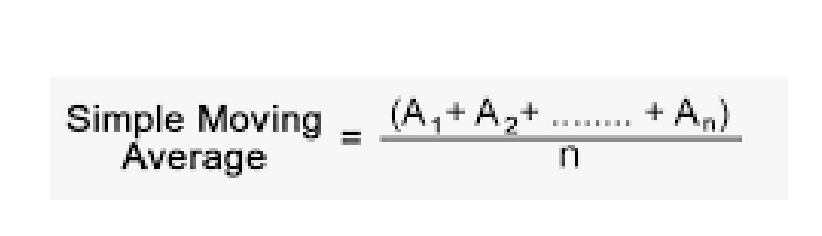
Weighted Moving Average
- Recent values are given more weight in calculating the forecast.
- Pro: Reflective upon updated data.
- Con: Complex calculations required.
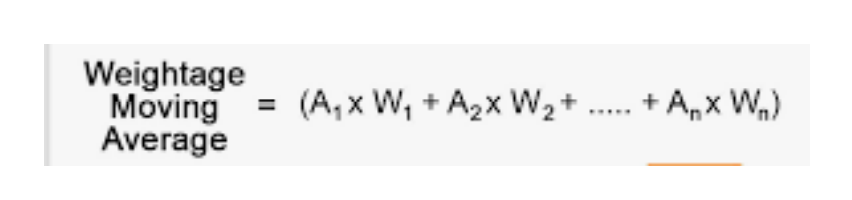
Exponential Smoothing
- Recent data with more weight.
- Pro: More weight within updated data.
- Con: Data includes potentially unnecessary data impacting total forecast.

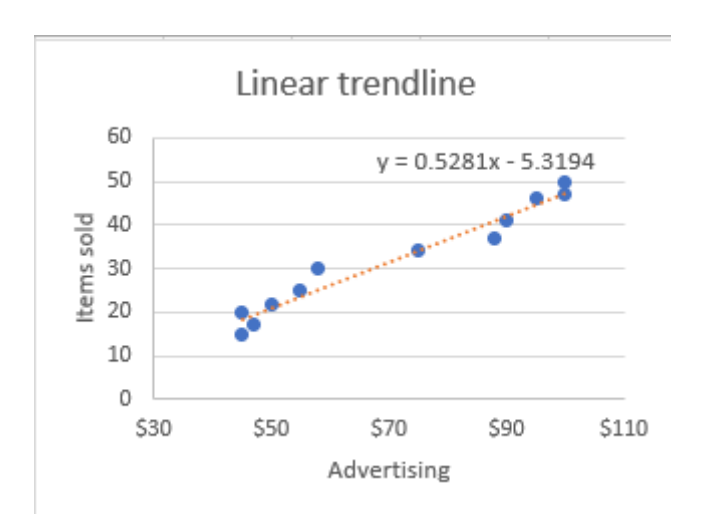
Linear Trend Line
- Straight line through a set of data through time series.
- Pro: Multiple statistics can be added.
- Con: Too much data with one independent variable.
Get Capella University Free Business Samples
BUS FPX 3007
BUS FPX 3011
BUS FPX 3021
BUS FPX 3022
BUS FPX 3030
BUS FPX 3040
BUS FPX 3050
BUS FPX 4012
